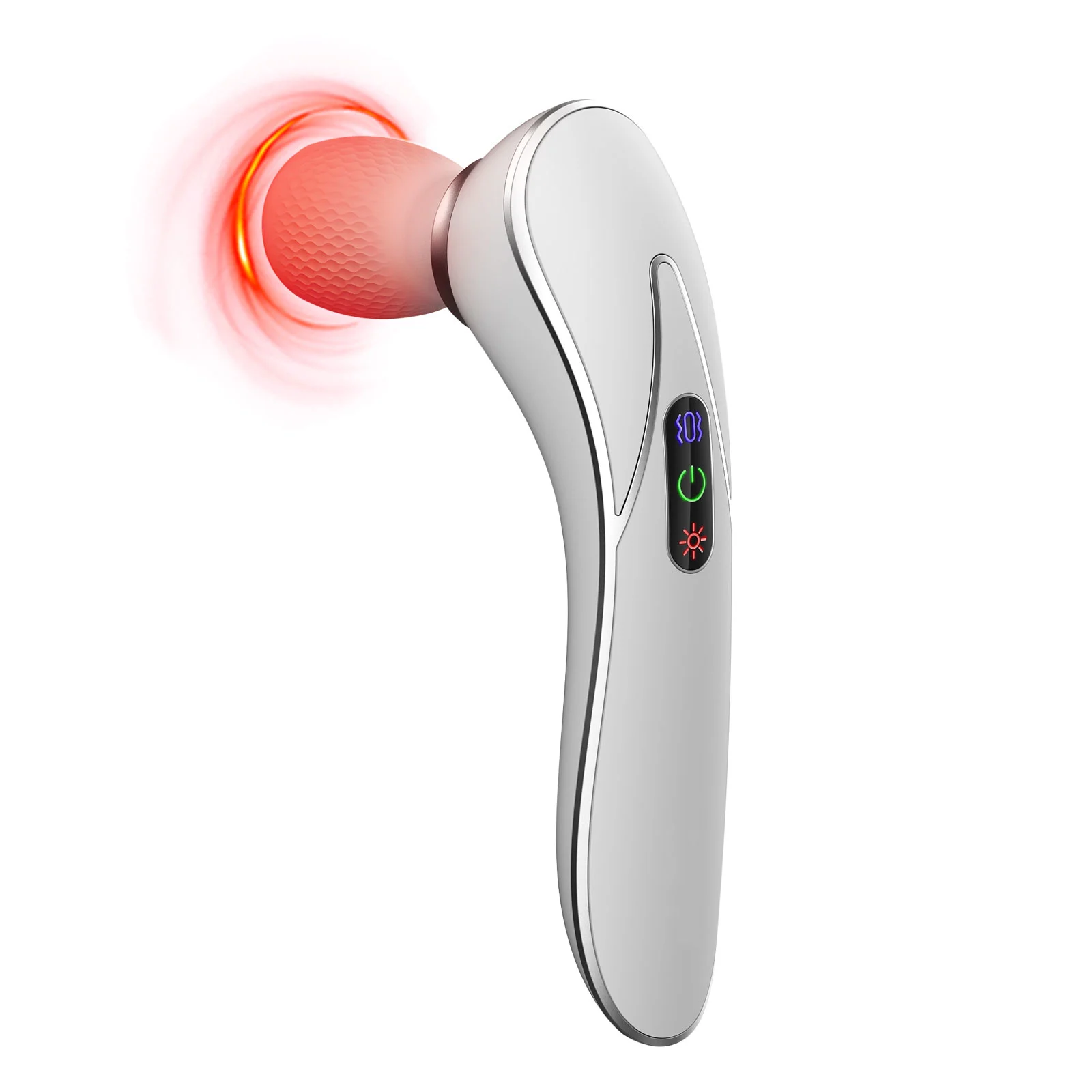
What Is an EMS Massager and Does It Really Work?
1. Introduction: Why EMS Massagers Are Blowing Up in 2024
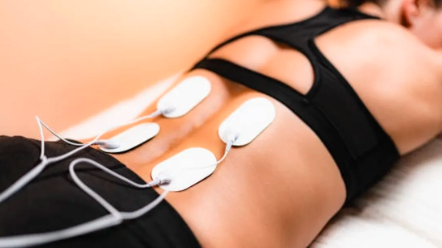
If you've ever seen a handheld device strapped to someone’s muscles at the gym or spa, there’s a good chance it’s an ems massager – a tech-driven way to give your muscles a workout without lifting a weight. Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) used to be the domain of professional physical therapy, but recently it’s become mainstream for home use, especially during downtime, recovery, or working from your desk.
What’s driving the trend? People want effective, non-invasive, hands-free tools. With stress-related pain rising and busy schedules, a tech gadget that activates muscles can't come soon enough. In this guide, we'll explore what EMS massage is, how it works, whether it can burn fat, who should avoid it, and whether it's better than alternatives like TENS. I'll also share tips on use frequency, safety, and choosing a legit ems massager for your home or B2B clients like spas and wellness spaces.
2.What Is an EMS Massager and How Does It Work?
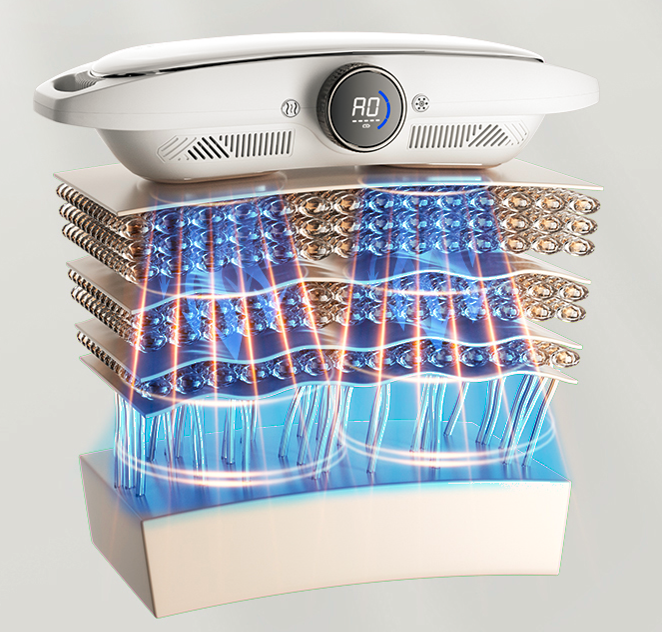
At its core, an ems massager sends tiny pulses through the skin to trigger muscle contractions—like your brain telling your muscles to move, but via wires instead of nerves. Those electrical impulses cause muscles to contract and relax without you having to flex physically.
Here’s what you get:
- Controlled muscle contractions for focus areas like thighs or abs
- Rehab-level recovery, because it mimics physiotherapy without the clinic
- Hands-free convenience, which appeals to office workers or home users
Long-tail keywords like “what is EMS massage” and “electrical muscle stimulation benefits” rank highly in searches, meaning people want to know how this tech can fit into their wellness routines.
Does EMS Actually Work? What Science and People Say
Yes—with caveats. EMS does cause muscle engagement, which can improve tone, circulation, and strength over time. Clinical studies demonstrate:
- Increased blood flow to treated areas
- Reduced post-exercise soreness
- Boosted muscle activation in areas that are hard to work out conventionally
But let’s be real—most of that research targets clinical settings or serious athletes. Does it help beginners lose belly fat? Not on its own. Is it good for recovery? Definitely. Real users often say things like: “It felt like my muscles got worked without me sweating.”
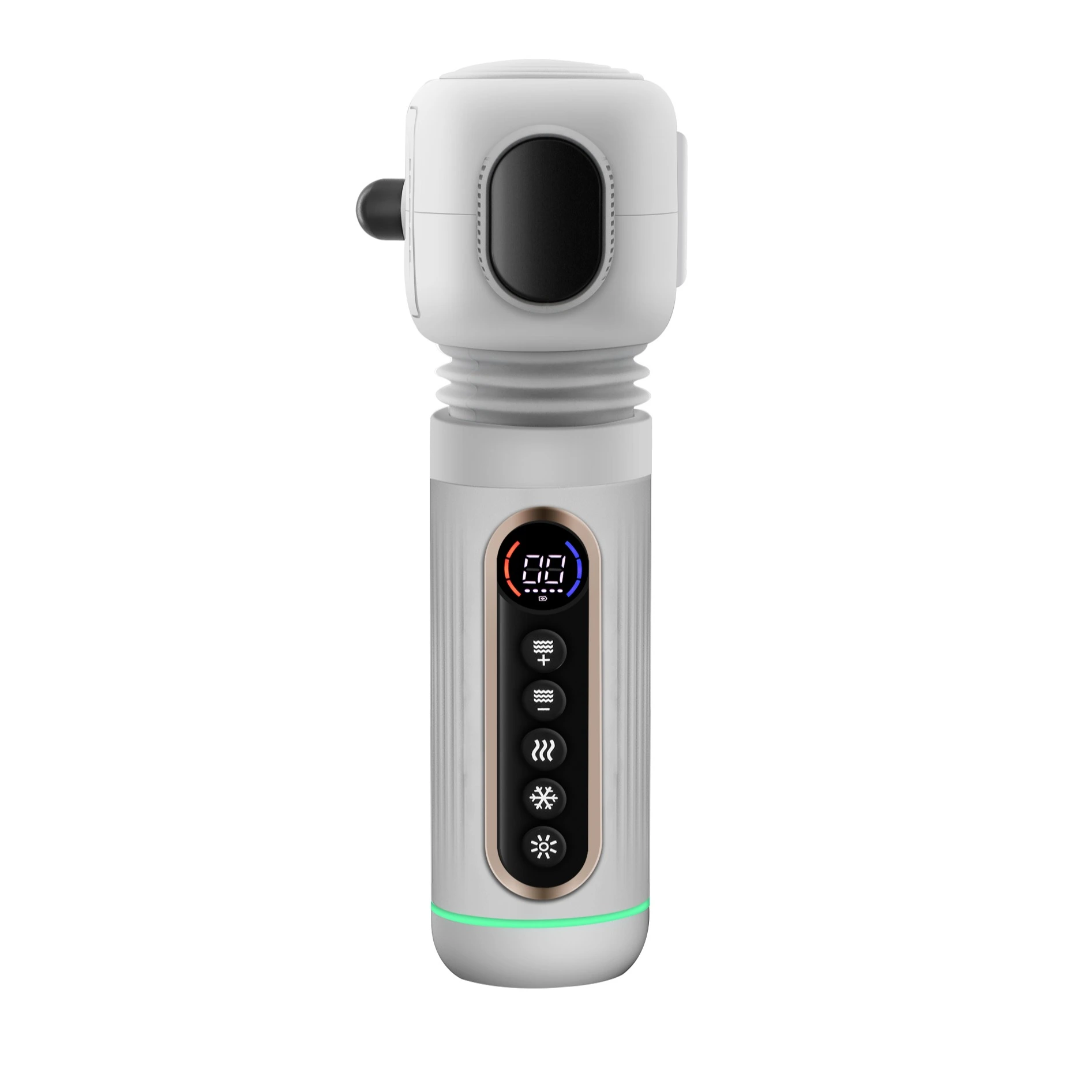
Pro tip: Devices like the L100 Hot & Cold EMS Sculptor by Emicool take this one step further. It combines electrical muscle stimulation with temperature therapy—hot mode improves blood circulation and muscle elasticity, while cold mode helps tighten skin and reduce post-workout swelling. Whether you're using it after a gym session or for aesthetic sculpting, it delivers targeted, tech-driven muscle care that traditional EMS pads just can’t match.
Can EMS Burn Fat or Belly Fat?
This is one of the most-asked questions. Technically, EMS can activate muscles, which burns calories—but the amounts are small. For fat loss, you need
- A calorie deficit
- Actual movement or resistance
- Consistency with EMS
If you’re strapped for time and can only squeeze in 20 minutes of EMS, you’ll activate muscles—but without movement or diet control, it won’t melt body fat. Long-tail searches like “can EMS burn fat” or “EMS belly fat reduction” show strong interest, but outcomes require combining EMS with lifestyle changes.
3. How Often Should You Use an EMS Massager?
Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Beginners: 15-20 minutes, 3x per week
- Advanced users or rehab patients: 30 minutes, 5–6x per week
- Maintenance use: daily, lower intensity, more like muscle “wake ups” than workouts
Overdoing it can cause muscle fatigue—not dangerous, but not ideal either. The sweet spot? Listen to your body. If your muscles feel fatigued the next day, give them rest.
Is EMS Safe? Side Effects & Who Must Avoid It
Generally, EMS is safe—especially if you use reputable devices. Still:
- People with pacemakers or metal implants should avoid it
- Pregnant women should consult doctors
- Common side effects: skin irritation under pads, temporary soreness
Long-term dangers? Rare if used properly. Important long-tails: “side effects of an EMS massager” and “what are disadvantages of electrical stimulation.” If pain, dizziness, or skin issues occur, stop use and seek advice.
4. EMS vs TENS: Which is Better?
Many wonder: EMS or TENS?
- TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) is for pain relief.
- EMS is for muscle activation.
So if your concern is muscle tone or circulation, go for EMS. If it's pain control, especially nerve-related, go TENS—or talk to a professional.
What Makes a Good EMS Massager for Home Use?
Here’s what matters:
Brands like Emicool have easy-to-clean pads, multiple modes, and app tracking—ideal for home wellness routines and B2B settings like fitness studios or rehab centers.
Heat feature: optional, but useful for stiff muscles
Battery life: 4+ hours on moderate usage
Safety certifications: CE, FCC, RoHS
Real Use Cases: Office Workers, Athletes & Rehab Patients
These use cases share a core truth: "Hands-free EMS lets me work while I recover." That convenience and multifunctionality matter more than most settings realize.

5.Final Thoughts: Is an EMS Massager Worth It?
If you:
- Want toning assistance
- Need daily muscle comfort and wake-up
- Prefer simple tech over heavy workouts
Then yes, an ems massager can help. But don’t expect miracle weight loss—synergy with movement and diet is key.
It’s a wellness tool: portable, science-backed, and easy to fit into routines. If you use it as part of consistent self-care, you’ll likely feel stronger, less sore, and more energized.
FAQ
- Can you use EMS every day?
- Yes—with low intensity and proper rest in between sessions.
- What are EMS massager side effects?
- Minor skin irritation, temporary soreness. Avoid if pregnant or with certain conditions.
- Can EMS burn calories or belly fat?
- It engages muscles and burns some calories—use it with diet and activity.
- Is EMS safe compared to gym workouts?
- Yes; risk of injury is lower—but resistance is limited to passive activation.
- Is EMS better than TENS?
- No—they serve different needs: endocrine vs pain relief.
An ems massager is not a replacement for exercise or doctor-prescribed treatments. It’s an accessible, supportive tool for muscle care—quiet, hands-free, and tech-friendly. If you want a practical, everyday wellness aid, EMS is worth trying.
What’s your experience with EMS? Head to the comments and share—your insight helps others find smart ways to recover.
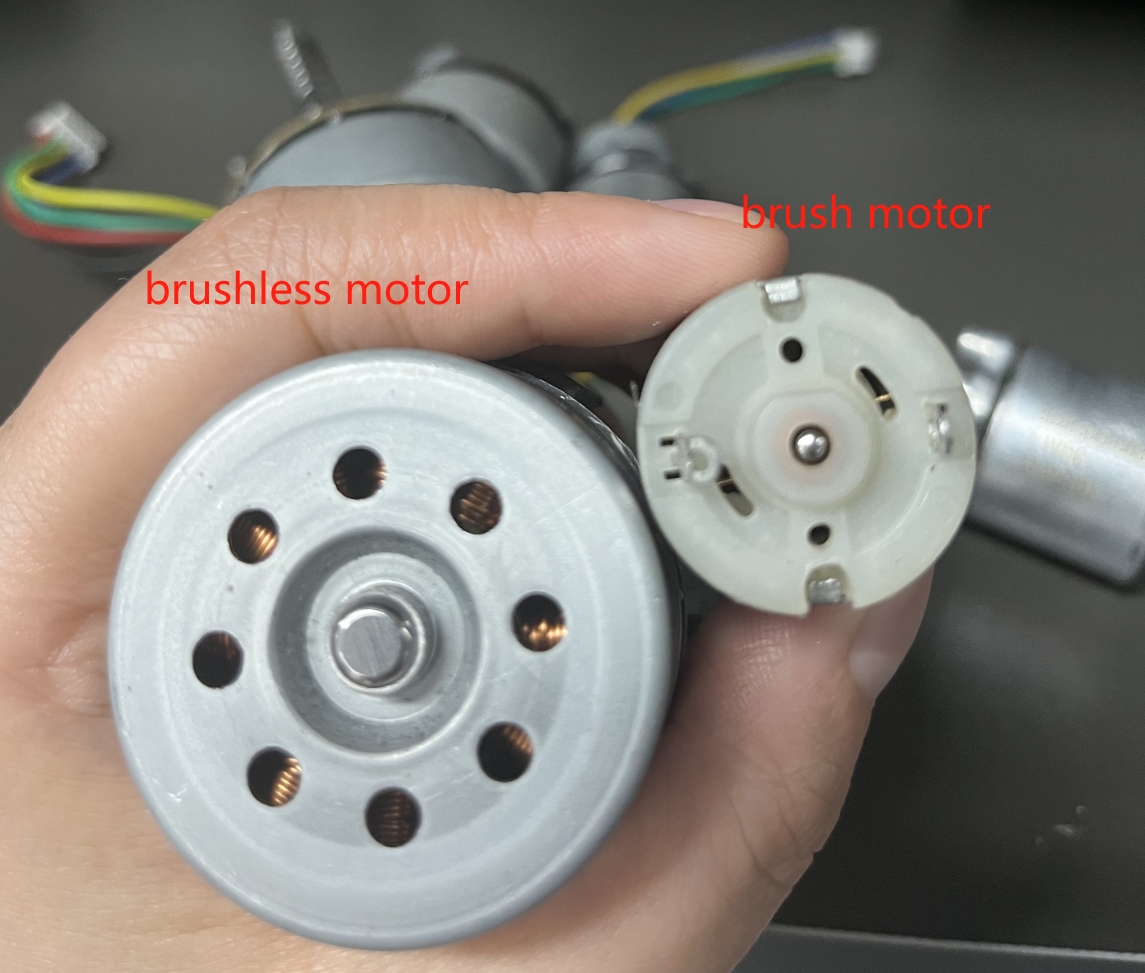
Brushless vs. Brushed Motors in Massage Guns: What Really Matters
NEWS